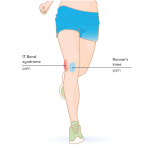
Anterior cruciate ligament or ALC injuries are prevalent and significant knee injuries, especially among sportsperson. These injuries often result from non-contact mechanisms such as sudden stops, pivoting, or improper landing techniques. Fortunately, many ACL injuries can be prevented by adopting targeted training programs and lifestyle modifications that focus on improving strength, flexibility, balance, and neuromuscular control.

Strength Training
Fortifying the musculature encircling the knee, especially the quadriceps, hamstrings, and gluteal muscles, is essential for alleviating strain on the ACL. Enhanced musculature offers superior support to the knee joint and more efficiently absorbs trauma. Exercises, including squats, lunges, and Nordic hamstring curls, are exceptionally helpful. Moreover, core strengthening exercises such as planks and bridges improve general body stability, facilitating optimal alignment during dynamic activities.
Neuromuscular Training
Neuromuscular training is designed to reduce the likelihood of injury by enhancing body mechanics and movement patterns. This includes drills that teach athletes how to jump and land safely with proper knee alignment.
For example:
- Plyometric exercises: Single-leg hops, skaters, and vertical jumps.
- Agility drills: Zigzag running or quick changes in direction.
These exercises train the body to control sudden movements that could otherwise strain the ACL.
Flexibility and Balance Exercises
Flexibility is crucial for preserving the whole range of motion in the knee joint. Dynamic stretches targeting the hamstrings, quadriceps, hip flexors, and calf muscles can improve mobility. Balance exercises such as a single-leg stand or using a balance board help enhance proprioception (awareness of joint position), which reduces the likelihood of awkward movements leading to injury.
Proper Technique and Biomechanics
Learning correct techniques for jumping, landing, cutting, and pivoting is vital for preventing ACL injuries. Risky movement patterns—such as inward knee collapse or hyperextension—can significantly increase stress on the ligament. Coaches and trainers should emphasize proper form during practice sessions to ensure these techniques become second nature.
Fatigue Management
Exercising while overly fatigued can lead to poor form and increase the risk of injury. Athletes should ensure they get adequate rest between training sessions and avoid pushing themselves beyond their physical limits. Effective recovery necessitates adhering to a balanced diet abundant in nutrients to facilitate muscle restoration and promote overall joint health.
Gender-Specific Considerations
Female athletes face an elevated risk of ACL injuries attributable to anatomical and hormonal disparities, with inequalities in neuromuscular control. Preventative programs tailored for female athletes often include additional focus on strengthening hip stabilizers and correcting landing mechanics to address these risk factors.
Structured Prevention Programs
Injury prevention systems such as FIFA 11+ have demonstrated a substantial reduction in ACL injury rates. These programs combine strength training, plyometrics, agility drills, and flexibility exercises into a structured warm-up routine lasting 15–20 minutes. Regular adherence to such programs can decrease injury risk by up to 75%.
Conclusion
Preventing ACL injuries requires a multifaceted approach that combines strength training, neuromuscular exercises, flexibility work, proper technique, and fatigue management. Integrating these strategies into standard training regimens enables athletes to markedly decrease their chance of ACL injuries while enhancing overall performance and promoting long-term joint health.
For enquiries and online appointments, send a message to www.DrAyyappanVNair.com/contact
For informative videos related to Shoulder problems and their treatment options, Sports Injuries and other orthopedic conditions, visit our YouTube channel Bangalore Shoulder Institute – https://www.youtube.com/@BangaloreShoulderInstitute